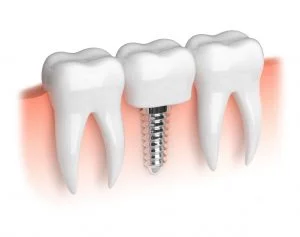
Making dental implants possible in case of bone volume deficiency
It is not possible to proceed with dental implant placement if there is a bone deficiency. A pre-implant bone grafting (prior to implant placement) or at the same time as implant placement will be necessary.
Why a bone graft ?
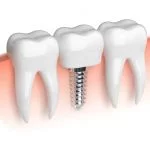
The jawbone must be dense enough and of good quality for successful implant anchoring. The structure of the implant resembles a small screw, the implant must be firmly anchored in the bone. The screw occupies volume and needs to be surrounded by the bone, otherwise a graft is required.
Commonly, patients who suffered from periodontal disease and a receded jaw have a very thin jawbone to accommodate an implant. A bone that is too thin can also appear following the loss of a tooth; in these cases, bone reconstruction is absolutely necessary.
How does it work ?
The technical solutions applicable for bone reconstruction differ according to the nature of the defect (height and/or thickness), its acuity (moderate or inferior defect, anterior or posterior sector) and also according to its location in the mouth.
In the case of severe bone deficiency, reconstruction should precede implant placement by 4 or 6 months as a waiting period. If the insufficiency is moderate, the reconstruction can be carried out simultaneously with the dental implant placement.
There are many bone reconstruction techniques available.
Preservation of the dental alveoli after extraction:
After tooth extraction, a reduction in bone volume occurs, which makes the placement of a dental implant difficult.
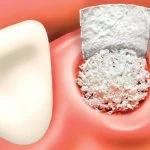
The procedure is known as ” Preservation of the alveoli after extraction ” and it consists of extracting the tooth and filling the gap with biomaterial bone (the void left in the bone after the tooth has been removed). This procedure ensures that the bone volume remains for implant placement. In some cases, the preservation of the extraction gap is not sufficient, a pre-implant bone reconstruction or during implant placement is unavoidable.
Sinus Lift:
Due to the presence of the sinus, which is a hollow cavity located above the premolars and maxillary molars, there may not be enough bone height available for implant placement in this area, a sinus lift then is deemed necessary.
Also called sinus-lift, the procedure consists of the elevation of the sinus membrane, a biomaterial is placed to support the membrane in the desired position. This will create an area of spontaneous ossification and bone cells will form the desired bone.
Guided bone regeneration:
This procedure allows the correction of moderate horizontal or vertical bone loss and avoids the need for a heavier procedure such as bone grafting.
It involves placing bone biomaterial or autologous bone in the form of chips at the site to be augmented and isolate it from the gum by a collagen membrane. Implant placement can be carried out simultaneously with guided bone regeneration whenever possible.
Bone grafting:
Regardless of the area, bone grafting makes it possible to achieve bone augmentation in height and in thickness according to volume of bone loss.
It is a transplantation of a volume of bone from one part of the body or from another person. Bone healing takes about 4 months, after which dental implants can be placed.
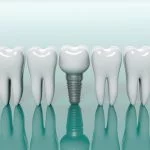
Bone reconstruction makes teeth implants possible.